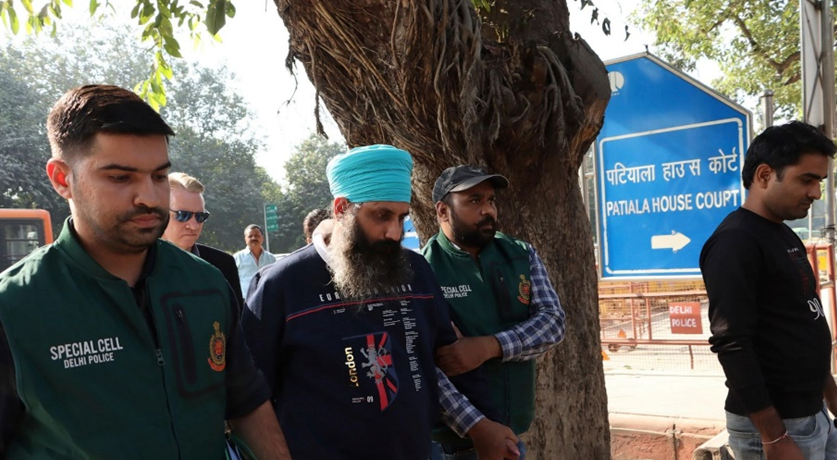
Extradition proceedings in Australia – both outgoing and incoming are governed by the Extradition Act 1988.
Extradition is a process by which one country apprehends and sends a person to another country for the purposes of criminal prosecution or to serve a prison sentence.
Australia is a party to over two dozen bilateral treaties with foreign states on extradition.
Australia is also a party to numerous multilateral treaties that contain provisions with respect to extradition.
In terms of international cooperation, extradition treaties that Australia has inherited from the United Kingdom can also apply and Australia is a party to a number of non-treaty agreements on a bilateral and multilateral level.
In accordance with Australia’s dualist approach to international law, these international instruments have effect in the Australian legal system through their incorporation in regulations to the Extradition Act.
Within Australia however, extradition laws also apply between the States and Territories. One State or Territory can apply to another State or Territory to have an accused or defendant extradited to the first State or Territory for legal prosecutions or a custodial sentence.
Our team specialise in criminal defence. Our role is to sit down with you and work out the strategy that will get you the best possible result. If you have any questions about this article or any other topic of law, please call our team of experts on 1300 066 669